
There are instances in which covered calls present higher than average risk and uncovered calls may present lower risks than most people think.
In fact, risk is not determined only by the nature of a strategy, but also on when the position is opened. In the case of the uncovered call, a swing to the point of resistance represents a point of opportunity (especially if string reversal signals are found at that point). A swing down to support represents adangerous place in the swing; as the price retraces back toward the center of the trading range, a previously ATM call with move to ITM, and this increases exercise risk and subsequent loss.
A few observations concerning risk should be the ruling factors in whether to consider writing uncovered calls. These are not for everyone, even in the best of circumstances; but if you are willing to accept a limited range of risks, keep these ideas in mind:
-
Volatility matters. The historical volatility of the underlying tends to expand and contract in cyclical patterns. When volatility is trending lower, all short positions become safer, even the uncovered call. The emphasis here is on historical volatility of the underlying and not on implied volatility of the option. Why? Because implied volatility is only an estimate, but historical volatility is a known factor.
-
Focus on short-term expiration. When expiration occurs in one to two weeks, time decay is at its highest point. This means you have a better than average chance of being able to buy to close at a profit due to time decay. The optimal point is on Friday before expiration. Between Friday and Monday, options on average lose one-third of remaining time value.
-
Probability is also a factor. The implied volatility can be checked as a measure of probability for an option being in or out of the money. Probability can be quantified with an analysis of the Greeks and based on your assumptions. To calculate volatility, use the free calculator provided by the CBOE, at CBOE Options Calculator
-
Be prepared to cover or close positions when the price moves against you. Even the best technical analysis is not always correct. Don’t let small losses turn into large losses and be willing to get out of the exposure by covering or closing the option. A third alternative is to roll forward, but this is not always wise. It keeps your collateral in pace for a longer time and if the underlying is trending against you, a minimum loss could grow into a large loss.
-
Avoid two dangerous dates. If you write uncovered calls, two dates should be avoided. Do not have the positions open in the week of ex-dividend. The dividend capture strategy involves buying calls and, if in the money, exercising them right before ex-dividend (and then closing the equity position on or after ex-date). This allows the trader to earn a quarterly dividend with a holding period of only one or two days. If you have an ITM short call, you could suffer early exercise. Also avoid having any short options open in the week that earnings are reported. A positive earnings surprise could make the stock price surge higher. Even though retracement is likely, when the uncovered call is deep ITM, early exercise is a distinct possibility and could translate to a substantial loss.
- Look for reversal signals.At any time, you have a short position open, it demands constant diligence. Prices can turn suddenly and unexpectedly, and by tracking price behavior every day, you can spot reversal as it begins and buy to close immediately to avoid problems. Many losses occur because traders do not pay attention and are taken by surprise. If your OTM option begins trending toward the money, it could be time to get out and avoid losses.
The ultimate signal
When should you open the uncovered call. There is one situation in which a short-term swing trade based on an uncovered call makes good sense.
Bollinger Bands is based on setting up the upper and lower bands at two standard deviations from the simple moving average of the middle band. Typically, traders look for price to move above the upper band or below the lower band to signal likely reversal. This is a worthwhile signal, but it can be made even stronger.
By changing the default to three standard deviations, you set up a near certainty of price decline. Price moving outside of three standard deviations never happens on most stock charts; but if you are looking for an opportunity to write uncovered calls, watch for price moving above the upper band with three standard deviations. (On the opposite side, if price falls below the lower band, it is an excellent time to write short puts.)
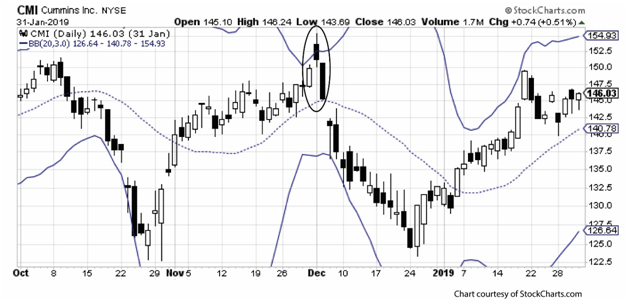
For example, the chart for Cummins (CMI) highlights a one-day move above the upper band. The default has been changed to three standard deviations. Although the one day the price moved above ended up closing below the upper band, this was a signal of a good time for a bearish trade. An uncovered call opened during the day the price was above the upper band had an excellent chance of becoming profitable. Price moved as high as $155 on the upper shadow. Selling a 155 uncovered call at that time would have been well timed. This was confirmed the following day with a second black candlestick. This became the third day of a strong candlestick reversal signal, the evening star. This forms with a white session, an upside gap, a black session, and then a third day with a lower black session.
As this signal predicted (along with the violation of the upper band), price fell sharply. Three weeks later, price was around $125, or 30 points lower than the high price above upper band.
Collateral requirements
This was a good ex ample of timing for an uncovered call. However, every trader considering uncovered calls also needs to be keenly aware of collateral requirements. Referring to the example, selling a 155 call requires a 20% deposit of collateral, or about $3,100, which must be kept in the margin account ifthe short position remains open. This restricts how many contracts can be opened at once. If you want to sell 10 calls, you will need $31,000 in collateral, for example.
To learn more about how margin requirements work, download the free CBOE Margin Manual, which explains margin requirements for every type of trade. You can also calculate required collateral easily, using the CBOE Margin Calculator.
Uncovered calls are risky trades, but timing and proximity mitigates the risk of poorly timed entry and exit. By being aware of price behavior, reversal signals, and strong signals (like the 3-standard deviation Bollinger signal), you improve your odds substantially of a successful and less risky trade.
Michael C. Thomsett is a widely published author with over 80 business and investing books, including the best-selling Getting Started in Options, coming out in its 10th edition later this year. He also wrote the recently released The Mathematics of Options. Thomsett is a frequent speaker at trade shows and blogs on his website at Thomsett Guide as well as on Seeking Alpha, LinkedIn, Twitter and Facebook.



There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.