
The Delta is one of the most important Options Greeks.
General
The delta of an option is the sensitivity of an option price relative to changes in the price of the underlying asset. It tells option traders how fast the price of the option will change as the underlying stock/future moves.
Option delta is usually displayed as a decimal value between -1 and +1. Some traders refer to the delta as a whole number between -100 and +100. Delta of +0.50 is the same as +50.
The following graph illustrates the behaviour of both call and put option deltas as they shift from being out-of-the-money (OTM) to at-the-money (ATM) and finally in-the-money (ITM). Note that calls and puts have opposite deltas - call options are positive and put options are negative.
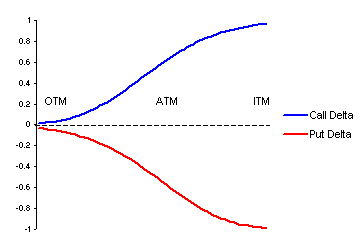
Call and Put Options
Whenever you are long a call option, your delta will always be a positive number between 0 and 1. When the underlying stock or futures contract increases in price, the value of your call option will also increase by the call options delta value. When the underlying market price decreases the value of your call option will also decrease by the amount of the delta. When the call option is deep in-the-money and has a delta of 1, then the call will move point for point in the same direction as movements in the underlying asset.
Put options have negative deltas, which will range between -1 and 0. When the underlying market price increases the value of your put option will decreases by the amount of the delta value. When the price of the underlying asset decreases, the value of the put option will increase by the amount of the delta value. When the underlying price rallies, the price of the option will decrease by delta amount and the put delta will therefore increase (move from a negative to zero) as the option moves further out-of-the-money. When the put option is deep in-the-money and has a delta of -1, then the put will move point for point in the same direction as movements in the underlying asset.
If you have a call and a put option, both for the same underlying, with the same strike price, and the same time to expiration, the sum of absolute values of their deltas is 1.00. For example, you can have an out of the money call with a delta of 0.36 and an in the money put with a delta of -0.64.
Delta Sensitivity
As a general rule, in-the-money options will move more than out-of-the-money options, and short-term options will react more than longer-term options to the same price change in the stock.
As expiration nears, the delta for in-the-money calls will approach 1, reflecting a one-to-one reaction to price changes in the stock. Delta for out-of the-money calls will approach 0 and won’t react at all to price changes in the stock. That’s because if they are held until expiration, calls will either be exercised and “become stock” or they will expire worthless and become nothing at all.
As expiration approaches, the delta for in-the-money puts will approach -1 and delta for out-of-the-money puts will approach 0. That’s because if puts are held until expiration, the owner will either exercise the options and sell stock or the put will expire worthless.
As an option gets further in-the-money, the probability it will be in-the-money at expiration increases as well. So the option’s delta will increase. As an option gets further out-of-the-money, the probability it will be in-the-money at expiration decreases. So the option’s delta will decrease.
It is important to remember that Delta is constantly changing during market hours and will typically not accurately predict the exact change in an option’s premium.
Delta as Probability
Delta can be viewed as a percentage probability an option will wind up in-the-money at expiration. Therefore, an at-the-money option would have a .50 Delta or 50% chance of being in-the-money at expiration. Deep-in-the-money options will have a much larger Delta or much higher probability of expiring in-the-money.
Looking at the Delta of a far-out-of-the-money option is a good indication of its likelihood of having value at expiration. An option with less than a .10 Delta (or less than 10% probability of being in-the-money) is not viewed as very likely to be in-the-money at any point and will need a strong move from the underlying to have value at expiration.
As mentioned, the sum of absolute values of delta of a call and a put with the same strike is one. This is in line with the probability idea. When you have a call and a put on the same underlying and with the same strike price, you can be sure that one of them will expire in the money and the other will expire out of the money (unless, of course, the underlying stock ends up exactly equal to the strike price and both options expire exactly at the money). Therefore, the sum of the probabilities should be 100% (and the sum of the absolute values of deltas should be one).
Just for clarification, delta and probability of expiring in the money are not the same thing. Delta is usually a close enough approximation to the probability.
Example
If the delta on a particular call option is .55, then, all other things being equal, the price of the option will rise $0.55 for every $1 rise in the price of the underlying security. The opposite effect is also seen as for every $1 decline in the price of the underlying the option will lose $0.55.
If the delta on a particular put option is -.45, then, all other things being equal, the price of the option will rise $0.45 for every $1 fall in the price of the underlying security. As with call options the obverse scenario is also true.
List of delta positive strategies
- Long Call
- Short Put
- Call Debit Spread
- Put Credit Spread
- Covered Call Write
List of delta negative strategies
- Long Put
- Short Call
- Put Debit Spread
- Call Credit Spread
- Covered Put Write
List of delta neutral strategies
- Iron Condor
- Butterfly
- Short Straddle
- Short Strangle
- Long Straddle
- Long Strangle
- Long Calendar Spread
Summary
- Positions with positive delta increase in value if the underlying goes up
- Positions with negative delta increase in value if the underlying goes down
- An option contract with a delta of 0.50 is theoretically equivalent to holding 50 shares of stock
- 100 shares of stock is theoretically equivalent to an option contract with a 1.00 delta
Watch the video:
Related articles:
- The Options Greeks: Is It Greek To You?
- Options Trading Greeks: Theta For Time Decay
- Options Trading Greeks: Vega For Volatility
- Options Trading Greeks: Gamma For Speed
Want to learn how to put the Options Greeks to work for you?






There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account. It's easy and free!
Register a new account
Sign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now