
A popular option strategy is the short strangle, which consists of selling an out of the money put and call. My personal backtesting and real trading experience is that this strategy on equity market ETF's or cash settled indices can increase portfolio diversification and if overlaid on a portfolio of underlying assets like mutual funds or ETF's can also increase total returns.
When you sell a strangle, you bring cash into your account. By doing so, you can "overlay" this trade on top of a portfolio consisting of ETF's or other investments without paying margin interest. Before we get too deep into the weeds, lets deal with the elephant in the room...you've heard strangles are risky. Is that true? The answer isn't that simple, as the trade isn't what measures risk, instead, it's the position size. Excessive leverage is risky, but strangles don't have to be traded this way. I'd encourage every option trader to not only consider the margin requirement of any particular option trade, but the notional risk. For example, think in terms of a 1 contract SPY strangle with SPY trading at $280 as theoretically being a $28,000 position (stock price X 100), similar to how buying 100 shares of SPY at $280 is a $28,000 position. When sized this way, a typical strangle will actual have less risk than the underlying asset.
With this in mind, let's look at a rough example of how we could implement this idea in a $100,000 account. First, we'll look at the performance of a 50/50 stock/bond portfolio that is rebalanced monthly since 2000.
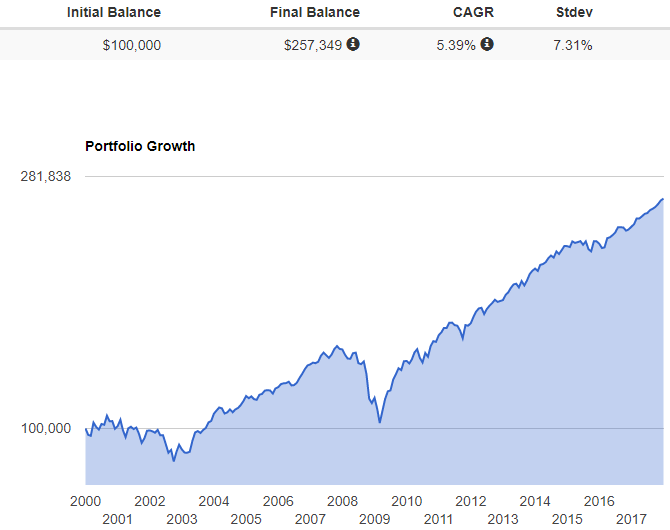
This portfolio would have returned a little over 5% annually, with a standard deviation of 7.31%, producing a Sharpe Ratio of 0.54.
Next, we'll add a 50% strangle allocation to this same portfolio. Yes, this equals 150%, which does make this concept only possible in a taxable margin account. The strangle allocation is based on our own backtesting platforms and proprietary rule sets and includes hypothetical trades on both SPY and IWM. A trader would sell 2 strangles on SPY in a $100,000 account to approximately replicate the concept.
Blue: Stock/Bond Portfolio
Red: Stock/Bond/Strangle Portfolio
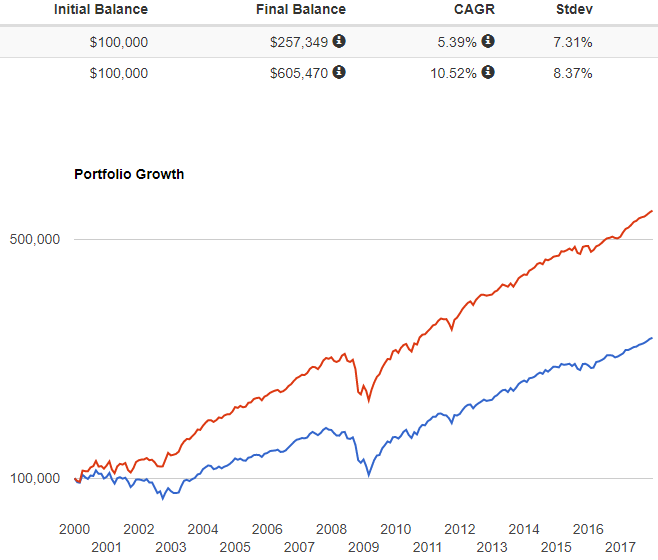
The 50/50/50 portfolio nearly doubles the annualized return to over 10%, and only with a modest increase in standard deviation to 8.37%. This increase in risk adjusted return substantially improves the portfolio Sharpe Ratio to 1.05. Even with a 50% increase in total portfolio allocation, the portfolio risk only slightly increases due to the low correlation of the strangle strategy to both stocks and bonds. This example is only meant to show the concept of an option overlay in action, and the potential benefits of doing so. Many other creative ideas could be implemented with other underlying assets and option strategies. My investment advisory firm, Lorintine Capital, currently implements these concepts in managed accounts as well as in one of our private funds, LC Diversified Fund. We are happy to have discussions with investors interested in a professionally managed solution, or ideas on how to implement this concept on their own.
Jesse Blom is a licensed investment advisor and Vice President of Lorintine Capital, LP. He provides investment advice to clients all over the United States and around the world. Jesse has been in financial services since 2008 and is a CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER™. Working with a CFP® professional represents the highest standard of financial planning advice. Jesse has a Bachelor of Science in Finance from Oral Roberts University. Jesse is managing the LC Diversified portfolio and forum, the LC Diversified Fund, as well as contributes to the Steady Condors newsletter.




Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.