
Options Delta Explained
For example, should a stock option price increase in price by 0.5c with a 1c increase in the underlying stock price then the option has a delta of 0.5.
Another way of looking at delta is as the probability of the option expiring in the money.
Some of the delta neutral strategies are ATM Long Straddle, Long Strangle and calendar spread.
Options Delta Math
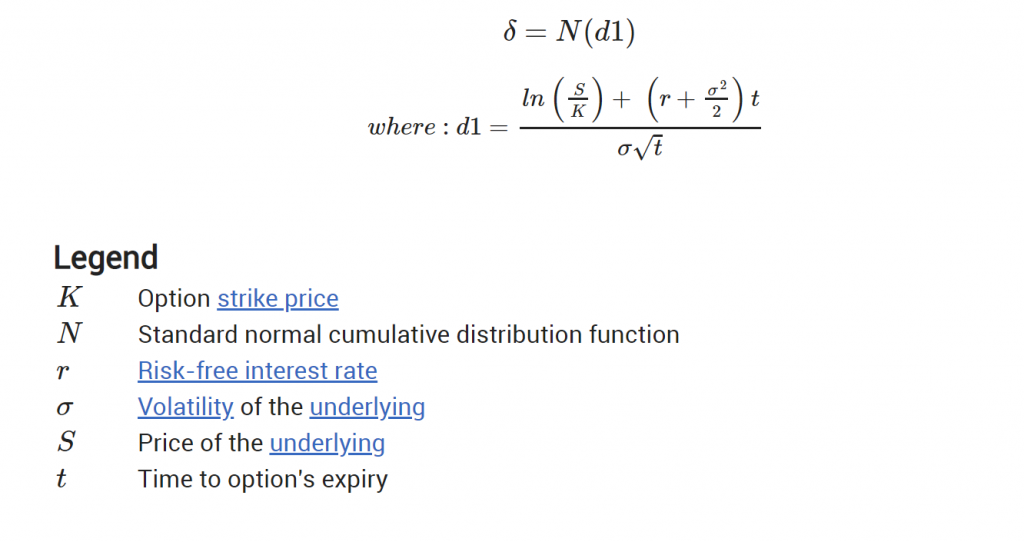
It's not necessary to understand the math behind delta (please feel free to go to the next section if you want), but for those interested delta is defined more formally as the partial derivative of options price with respect to underlying stock price.
The formula is below (some knowledge of the normal distribution is required to understand it).
Delta is superficially the most intuitive of the options greeks. Even the newest beginner would expect the price of an option, giving the right to buy or sell a particularly security, to change with the security’s price.
Let’s look at an example with call options on a stock with $120 stock price as it rises higher (by $10 to $130, say).
In the money options – those with a strike price less than $120 – would become even more in the money. Thus their value to the holder would increase – the probability of them remaining in the money would be higher – and hence, all other things being equal, the option price would rise.
Out of the money and at the money options – those with an exercise price of $120 or greater – would also rise in value. The probability of, say, a $140 option expiring in the money would be higher if the stock price was $130 compared to $120. Hence its value would be higher.
Similar arguments can be used with put options: their value rises/falls with the fall/rise of the underlying (the only difference being put options have negative delta versus call options, whose delta is positive).
But the extent of this sensitivity – i.e. delta – and how it relates to expiration length, price, and volatility is quite subtle. Let’s look at it in more detail.
Delta for Short vs. Long Options
Options can be bought or sold. Depending on which side of an option trade an investor is on, the delta of that option will adjust accordingly.
For long options, delta values are positive for calls and negative for puts. A bought (long) call will have a delta between 0 and +1, rising as the option becomes more in-the-money. A purchased put option will have a delta between 0 and -1, with delta falling the further the put is positioned in-the-money.
The inverse is true for shorting options. When selling call options, delta scores will be a negative value, between 0 and -1. This is true because a short call option position will increase in value as the underlying security falls - the writer of a call option will benefit as the underlying security falls. The other way to look at this is to understand that a call option has a positive delta, but that the seller/writer of that call option has the inverse exposure.
Similarly, put options, which provide a delta exposure of -1 to 0 for the owner, expose the seller/writer of the put option to a positive delta between 0 and +1.

How Does Options Delta Change Over Time?
The effect of time on delta depends on an option’s ‘moneyness’.
In the money
All other things being equal, long dated in the money options have a lower delta than shorter dated ones.
In the money options have both intrinsic (stock price less exercise price) and extrinsic value.
As time progresses the extrinsic reduces (due to theta) and the intrinsic value (which moves in line with stock price) becomes more dominant. And so the option moves more in line with the stock, and hence its delta rises towards 1 over time.
Out of the money
All other things being equal, short dated OTM/ATM options have a lower delta than longer dated ones.
A short dated out of the money option (especially one which is significantly OTM) is unlikely to expire in the money, a fact that is unlikely to change with a 1c change in price. Hence its delta is low.
Longer dated OTM (Out Of The Money) options are more likely to expire in the money – there is a longer time for the option to move ITM (In The Money) – and hence their value do move with stock price. Hence their delta is higher.
At the money
There is no effect of time on the delta of an at the money option.
How Does Options Delta Change With Implied Volatility?
Again the effect of implied volatility changes on delta depends on moneyness.
In The Money
As we saw above in the money options’ value comprise both intrinsic and extrinsic amounts.
In general the higher the proportion of an option’s value that is intrinsic (which moves exactly in line with stock price) and extrinsic value (which doesn’t), the higher its delta.
Increases in IV increase the extrinsic value of an option and so, as intrinsic value isn’t affected by implied volatility, increases the percentage of the option’s value that is extrinsic. This resultant reduction in the intrinsic value as a proportion of the whole, reduces the option’s delta as above.
Out Of The Money
Out of the money options have only extrinsic value, which is driven by the probability of it expiring in the money.
A higher volatility suggests there is a greater chance of the option expiring ITM (as the stock is expected to move around more) and hence delta increases.
At the money
ATM options have a delta of approx. 0.5, which is unchanged as volatility changes.
Effect Of Changes Of Price On Delta
One of the other subtleties of delta is that it in itself changes value as the underlying security’s price changes.
The extent to which this occurs is another of the options greeks: gamma. This is the change in delta resulting in in a 1c change in stock price.
Gamma for long options holders is positive whereas it is negative for short positions, meaning it helps the former and penalises the latter. It is also at its highest absolute value near expiration. (See here for more discussion on gamma).
Conclusion
Delta is an important greek as it reflects an option holder’s exposure to one of the main variables: the price of the underlying security.
Whilst one of the easiest option concepts to understand, its behavior resulting from changes to other variables such as time, IV and underlying price is more complex.
It is vital for an options trader to understand these concepts.
About the Author: Chris Young has a mathematics degree and 18 years finance experience. Chris is British by background but has worked in the US and lately in Australia. His interest in options was first aroused by the ‘Trading Options’ section of the Financial Times (of London). He decided to bring this knowledge to a wider audience and founded epsilonoptions.com in 2012.
Related articles:
- Options Greeks: Theta, Gamma, Delta, Vega And Rho
- Options Theta Explained: Price Sensitivity To Time
- Options Gamma Explained: Delta Sensitivity To Price
- Options Vega Explained: Price Sensitivity To Volatility
- Options Rho: Sensitivity To Interest Rates






There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account. It's easy and free!
Register a new account
Sign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now