
Part of approaching markets probabilistically is ensuring that your trades, on average, make money. Traders use several metrics like risk/reward ratio, Sharpe ratio, profit factor, and win rate to estimate what they should expect from their average trade.
However, your risk/reward ratio and win rate are the basic building blocks you'd use to understand how your average trade performs.
From your risk/reward ratio and win ratio, we can make a rough calculation of your expected value or how much you can expect to earn from your average trade over a large sample size. Knowing your expected value allows you to project how your portfolio will perform over time.
Before that, let's settle on what your win rate and risk/reward ratio mean in trading.
What is a Win Rate in Trading?
Put simply, your win rate is the percentage of your trades that show a profit. A 60% win rate trader makes money on 60% of his trades.
Too many novices are taken by the allure of a high win rate. After all, how many advertisements for Forex trading courses advertise a high (80%+) win rate? But we must remember that a win rate only takes into account the percentage of trades you win, not how much you win or lose on each trade.
You can quickly devise a very high win-rate trading "system" with little work. Simply buy an option or stock and immediately submit a limit order to sell it one tick higher than your purchase price. Have no stop loss.
Most of the time, the security will trade above your purchase price, and you'll win almost all of your trades. However, because you have no stop loss, sometimes you'll lose most or all of your capital employed.
You probably don’t need telling that this is a very poor and unprofitable trading strategy despite its high win rate.
Conversely, a low win rate is undoubtedly not a disqualifying factor for the quality of a trading system. Futures trend followers like the Turtle traders of the late 1980s are a famous example of traders who win around 30% of their trades yet are profitable because their winning trades are way bigger than their losing trades.
What is a Risk/Reward Ratio in Trading?
Just a technicality here to avoid confusion. While the nomenclature in trading culture is to refer to this metric as a risk/reward ratio, what traders are typically referring to is the reward/risk ratio, which places 'reward' as the numerator. From here on out, we'll refer to the reward/risk ratio. Just keep in mind that when most traders say "risk/reward," they're really talking about reward/risk.
As options traders, we have the gift of being able to shape our reward/risk ratio in nearly any way we'd like. Unlike delta one markets like equities and futures, it's much easier to fix our risk and reward levels using options spreads surgically.
If you want a 2.0 reward/risk ratio, you can likely construct that using a vertical spread. If you're looking for substantial home runs, you can potentially find a profitable way to get long out-of-the-money options while remaining sensible.
The primary thing to keep in mind is that you subsidize your risk/reward ratio with your win rate. In other words, you can't have a high win rate and a high risk/reward ratio or vice versa. We'll get into the specifics as to why soon.
You can calculate your reward/risk ratio you need two pieces of information:
-
How much you intend to risk on a given trade
- How much you estimate to win should the trade work out in your favor.
Perhaps we intend to risk $100 per trade when we lose and gain $150 when we win. The calculator is as simple as $150/$100 = 1.5. 1.5 is our reward/risk ratio, meaning we can expect to earn 1.5x more on our winning trades than on our losing trades.
While a positive reward/risk ratio is often sold as a holy grail, the options market is not that simple, and you cannot approach options trading the way a delta one equity trader does. After all, buying out-of-the-money calls yields a very high reward/risk ratio, often higher than 10. But your likelihood of actually winning those trades is very low. After accounting for the low win rate, it's frequently an unprofitable strategy.
On the other hand, strategies like selling volatility can have low reward/risk ratios of 0.2 and still be profitable. Sure, your losing trades will be huge, but you'll win most of your trades. Some short-volatility traders can get so in tune with the current market cycle that they can go 20-30 trades before they have one that blows up in their face.
So we cannot view our reward/risk ratio in a vacuum. We'll demonstrate this more when we talk about expected value, which combines reward/risk and win rate.
The point here is that reward/risk, and win rate is linked. You can't really manipulate one without affecting the other. If you want a high win rate, you must accept an unfavorable reward/risk ratio and vice versa.
There's no free lunch in markets where you can achieve a 3:1 reward/risk ratio with a 70% win rate, save for rare illiquid, and unscalable situations. This should be self-evident, too. If a trader can consistently make trades in liquid markets with an expected value like this, he'd own the entire capitalization of the stock market in no time.
While most traders direct the strong form of the efficient markets hypothesis, few would deny that markets are efficient enough to deny you opportunities to print money with little risk by allowing you to systematically and scalably trade with a high risk/reward ratio and a high win rate.
Let's demonstrate this, too, so you can viscerally understand how you can't have the best of both worlds regarding reward/risk and win rate.
What is Expected Value in Trading?
Imagine I offered you even money to bet on a fair coin flip. The expected value of this game is zero.
Let's say you pick tails. Each time the flip comes up tails, you win a dollar, each time it comes up heads, you lose a dollar. Because the odds of tails and heads hitting are even at 50%, you can expect to make $0 per flip over a large sample size of coin flips.
However, if I altered the odds so that you win $2 for tails and lose $1 for heads, this game's expected value is now $0.50 per flip.
We can calculate this with a straightforward formula:
(Amount won per trade * probability of winning the trade) - (Amount lost per trade * probability of losing the trade)
It’d look like this for our updated coin flip game:
($2 * 0.50) - ($1 * 0.50) = $0.50
Hopefully, it goes without saying that if someone ever offers you odds like these, take them all day.
This is expected value in a nutshell. Wikipedia puts it like this if you want a more technical definition:
The expected value is the arithmetic mean of a large number of independently selected outcomes of a random variable.
Demonstrating Expected Value in Trading
The combination of reward/risk ratio and win rate is your expected value. It's a formula that answers the question, "given my probability of winning a trade, how much can I expect to win per trade, over a large number of trades, given my reward/risk ratio?"
We'll use the example of a 3:1 reward/risk ratio and a 70% win rate, risking $100 per trade. First, we calculate the expected value of the average trade using the same simple formula we used for our coin example:
(Amount won per trade * probability of winning the trade) - (Amount lost per trade * probability of losing the trade)
Our formula would look like this:
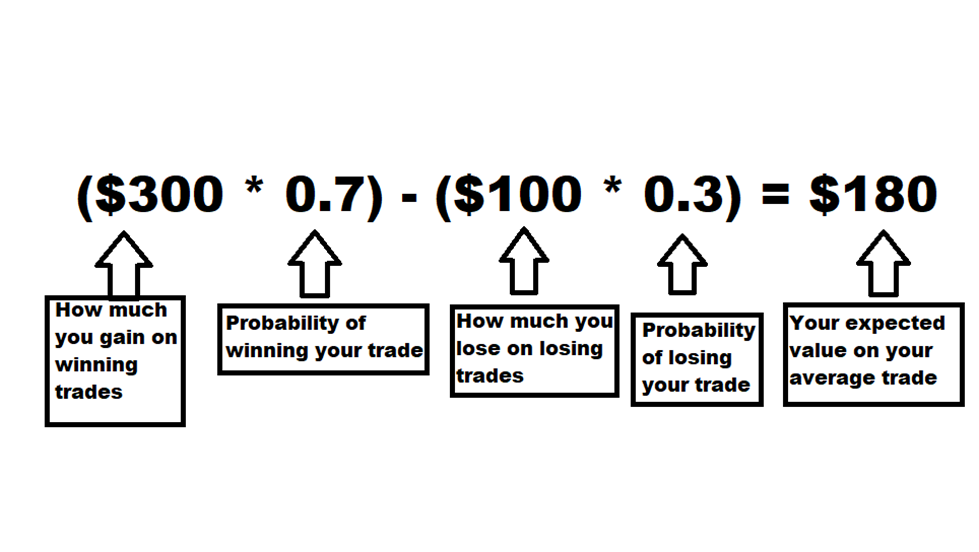
Remember that this is an entirely unreasonable combination of win rate and reward/risk and is meant to demonstrate the folly of searching for the golden system that gives you both.
Doing an elementary compounding calculation in Excel also shows you this. If we start with a bankroll of $10,000 and risk 1% (or $100 as in the example above) and make four trades a week, at the end of the year, our bankroll would be 360K, representing a 3,775% annual return.
Of course, this is based on an expected value of $180 per trade without any variance calculations, but it shows how the market works. You can have a high reward/risk or high win rate. Pick one.
Bottom Line
To summarize:
-
Win rate refers to how often you win your trades. High win rates typically mean unfavorable reward/risk ratios and vice versa.
-
The market lets you choose if you want a high win rate or a high reward/risk ratio, but not both, except in the rarest of cases.
-
Knowing and understanding both your win rate and your reward/risk ratio is essential, and you can't solely rely on one metric.
- Expected value represents the combination of win rate and reward/risk and tells you what you can expect to earn on your average trade.



There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.