
Should I place all my contracts at one strike and expiration, or split it up for diversification? Should I wait until expiration as my natural exit, or roll early? Should I handle winning trades the same way as losing trades? Should I only sell enough contracts to be fully cash secured, or use leverage?
In this article, I’m going to address the question of choosing strikes based on delta, while keeping the other variables constant, in order to show some historical performance comparisons of SPX put options from 2001-2018. Whenever I make trading decisions, I always remind myself of a couple quotes from W.E. Deming…
“In God we trust, all others must bring data.”
“Without data you’re just another person with an opinion.”
Assumptions held constant for the following backtests…
- Product: SPX
- Period: 2001-2018
- Entry: 30 DTE
- Exit: 80% of credit received, or 5 DTE, whichever comes first
- Position Sizing: 100% notional/cash secured (no leverage)
- Collateral yield: 0%
- Commissions and slippage: Not included
Based on those assumptions, here’s the data for trades placed at different deltas.
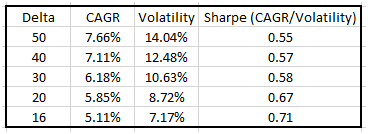
Key observations:
- Higher risk has historically resulted in higher reward…As strikes move away from at the money (ATM), volatility and annualized returns both decline. This is what we would have expected to see in a world of not perfectly, but highly efficient markets.
- Sharpe Ratio’s increased with out-of-the-money (OTM) options. This is what I find most interesting and worthy of further discussion.
Why would there be higher Sharpe Ratio’s with OTM options, and is there any opportunity based on this data? Research from AQR has come to similar conclusions that Sharpe Ratios tend to increase the further out of the money an option is sold. This might be for the same reason that we see a linear decrease in historical Sharpe Ratios for US treasuries the further out on the yield curve you go (i.e., comparing Sharpe Ratios of 1/2/5/10/30-year treasuries): Aversion to and/or constraints against the use of leverage.
If you’re an investor who is unwilling or unable to use leverage, your only choice to maximize expected returns is to sell the riskiest option (ATM) and buy the riskiest treasury bond (30-year). This being a common theme among market participants can create market forces that impact prices. But if you are willing and/or able to use leverage, you could simply lever up OTM put options or shorter-term treasury futures to your desired risk level, and get paid more per dollar risked. Isn’t that the objective…the most gain with the least pain?
Of course, risk cannot be eliminated…only transformed, and leverage creates risks of its own and should be used responsibly. Unfortunately, it too often isn’t. As I wrote in a recent article, excessive leverage is the number one mistake I see retail and even occasionally “professional” investors make. In our Steady Momentum strategy, we sell OTM puts and lever up to around 125% notional to give us a similar expected return as ATM puts with slightly less volatility. We also collateralize our contracts with short and intermediate term bonds instead of cash, as collateral ends up being a significant portion of total returns with put selling strategies.
Jesse Blom is a licensed investment advisor and Vice President of Lorintine Capital, LP. He provides investment advice to clients all over the United States and around the world. Jesse has been in financial services since 2008 and is a CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER™ professional. Working with a CFP® professional represents the highest standard of financial planning advice. Jesse has a Bachelor of Science in Finance from Oral Roberts University. Jesse manages the Steady Momentum service, and regularly incorporates options into client portfolios.






There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account. It's easy and free!
Register a new account
Sign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now