
Options may also possibly offer a better return on investment, or ROI, compared to making outright long or short bets using the underlying stock or derivatives.
As its name suggests, a bull call spread may be used when the investor is bullish on a market and wants to potentially profit from higher prices.
Description of the Bull Call Spread Strategy
The strategy uses two options: a long call and a short call to provide a limited risk/limited profit trade.
The long option is purchase closer to “the money,” which is the current market price of the underlying asset. The short option is sold at a higher price, or further “out of the money.”
The maximum profit potential of the trade is easily calculated. To determine maximum profit potential, simply take the difference between strike prices and subtract the premium paid for the spread, also factoring any any commissions or fees.
The maximum loss potential is even easier to calculate. The maximum amount of capital that can be lost is the total premium paid for the spread plus any commissions or fees.
For example: Suppose you are bullish on stock XYV, which is currently trading at $40 per share. You believe that the stock is likely to rise in the next 30-60 days, and want to take a bullish position in the shares. Rather than buying 100 shares of XYZ and hoping it moves higher, you decide to initiate a call spread by purchasing the $40 call and selling the $44 call for a net premium of $1.00. The options have 60 days until expiration.
If the price of XYZ were to climb to $45 at expiration, the bull call spread would reach its full intrinsic value of $4.00 (calculated as the difference between the two strike prices of $40 and $44). Because you paid $1.00 for the spread, your net profit would be $3.00.
Now suppose your forecast about the stock was wrong, and the share price declines to a level of $38 at expiration. In this case, both options would simply expire worthless and your loss would equal the maximum of the $1.00 premium paid.
In another scenario, suppose that the stock climbs, and is trading at $42 per share at expiration. In this case, the profit cold be calculated as the intrinsic value of the spread ($2.00) minus the premium paid ($1.00) for a net profit of $1.00.
The break-even of a bull call spread is calculated as the long call strike price minus plus the premium paid. Using the above example, the break-even would therefore be calculated as $41 ($40 long call strike price plus $1.00 premium paid).
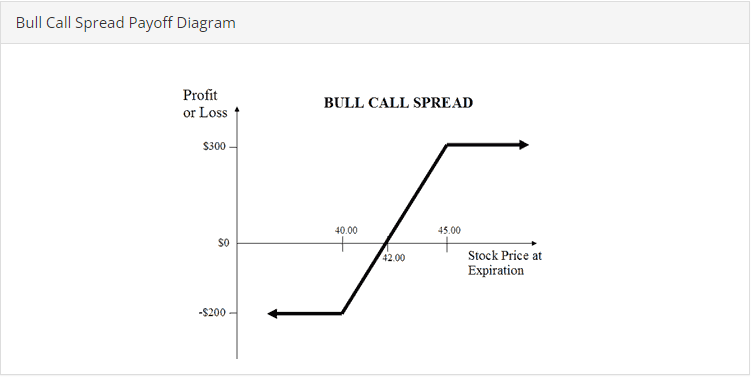
Bull Call Spread Payoff Diagram
When to put it on
A bull call spreae may be out on at varying times based on the trader’s goals, risk tolerance and market conditions. There are, however, a few simple rules of thumb to consider. Because the spread is bullish, it is important to try to initiate it when prices are likely to continue rising or stage a bullish reversal.
A market that has recently broken out to fresh highs on strong volume could potentially be a good candidate for a call spread. Such a market move could potentially allow the trader to capitalize on an extended upward move or resumption of an uptrend.
Another potentially good place to initiate a call spread is when a market declines into previous support levels or pulls back within a larger uptrend. For a market that has been beaten down and declined to levels where it previously found buyers, bargain hunters could step in and fuel a reversal back to the upside.
For a market that has been trending higher on the longer time frames, a pullback into a support level may provide an opportunity to get long the market before it resumes the trend higher.
Pros of the Bull Call Spread Strategy
The bull call spread has several advantages. Perhaps the biggest advantage is the defined risk of the position. No matter what happens, a trader can not lose more than their premium paid.
Another major advantage may be a higher return on investment. The cost to put on a bull call spread may be considerably less when compared to the cost of holding an outright long position in the stock or contract.
Cons of the Bull Call Spread Strategy
There is no free lunch when it comes to options trading, and the bull call spread is no exception. The spread does come with some disadvantages as well that should be carefully considered. The biggest disadvantage of a bull call spread is the effects of time decay, known in the options world as “theta.”, one of the Options Greeks.
Because options have an expiration date, they will lose value with the passage of time all other inputs remaining constant. In other words, you not only have to be right about market direction, but you also have to be right about the timing.
The theta of the bull call spread would become positive if both options are In-The-Money. This would increase the probability of success, but also reduce the profit potential because ITM spreads cost more.
Bull call spreads may also require a sizable market move to turn a profit. Because of this, it may be best to only consider using a bull call spread when a substantial move is expected.
Risk Management
Managing a bull call spread is fairly straight forward. How you manage the risk is a matter of preference. One simple method for managing risk is to determine an exit point at which you will close the position. For example, if you paid a $1.00 premium for a bull call spread, you may simply exit the spread if the value falls to $.50.
This method is simple but can be highly effective, especially when profit potential on the spreads is at least four times the risk.
Possible Adjustments
For spreads that are not going according to plan, there are other adjustments that can also be made. Selling the spread back to the market and purchasing the same spread at a further expiration is one such method.
The bull call spread is a limited risk and highly versatile position that can be utilized by even novice traders. The spread can potentially provide significant profit potential with little stress. With its numerous advantages, the bull call spread should be a part of every trader’s arsenal.
The Bottom Line
The bull call spread is a suitable option strategy for taking a position with limited risk and moderate upside. In most cases, a trader may prefer to close the options position to take profits (or mitigate losses), rather than exercising the option and then closing the position, due to the significantly higher commission.
It also offers great flexibility in terms of strike selection and expirations.
About the Author: Chris Young has a mathematics degree and 18 years finance experience. Chris is British by background but has worked in the US and lately in Australia. His interest in options was first aroused by the ‘Trading Options’ section of the Financial Times (of London). He decided to bring this knowledge to a wider audience and founded Epsilon Options in 2012.
Subscribe to SteadyOptions now and experience the full power of options trading at your fingertips. Click the button below to get started!
Join SteadyOptions Now!






There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account. It's easy and free!
Register a new account
Sign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now